Pleomorphic Adenoma
Understanding Pleomorphic Adenoma: Causes and Management
Description: Pleomorphic adenoma is a type of benign tumor that develops in the salivary glands. This blog aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of pleomorphic adenoma, including its causes, diagnostic methods, clinical and radiological features, pathological characteristics, and management options.
Introduction:
Pleomorphic adenoma, also known as benign mixed tumor, is the most common type of tumor affecting the salivary glands. It typically develops in the parotid gland, which is the largest of the salivary glands located in front of the ear. However, it can also affect other salivary glands, including the submandibular and minor salivary glands. Despite being benign, pleomorphic adenoma can cause significant discomfort and disfigurement. This blog aims to provide a detailed overview of this condition, including its causes, diagnosis, and management.
What is it?
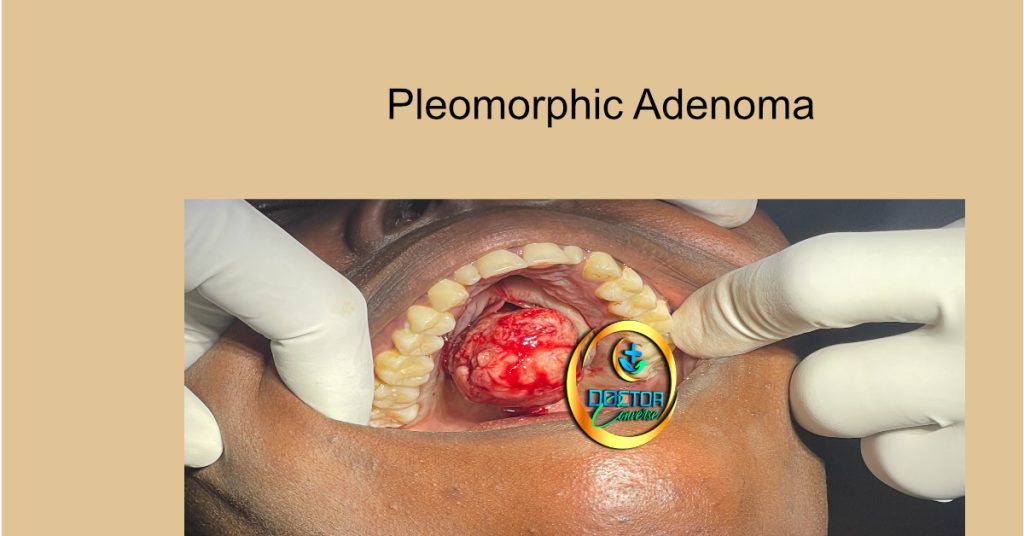
Pleomorphic adenoma is a type of benign tumor that arises from the epithelial cells lining the salivary glands. The tumor is characterized by a mixed appearance, with cells displaying different morphologies and structures, including ductal and myoepithelial cells. The tumor can vary in size and shape, ranging from a few millimeters to several centimeters.
What is Aetiology?
The exact cause of pleomorphic adenoma is not well understood. However, certain risk factors have been identified, including age, gender, radiation exposure, and genetic factors. Studies have shown that women are more commonly affected than men, and the tumor is more prevalent in individuals aged between 30 and 60 years.
How to diagnose?
Diagnosing pleomorphic adenoma requires a combination of clinical, radiological, and pathological assessments. The clinical features may include a painless, slow-growing lump in the salivary gland area, which can be palpated during physical examination. Radiological imaging, such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI, may be used to confirm the presence of the tumor and evaluate its size and location. Finally, a biopsy of the tumor tissue is necessary to confirm the diagnosis and rule out malignancy.
Differential Diagnosis:
The differential diagnosis of pleomorphic adenoma includes other types of benign and malignant tumors affecting the salivary glands. These may include Warthin’s tumor, mucoepidermoid carcinoma, adenoid cystic carcinoma, and acinic cell carcinoma. A proper diagnosis is essential to determine the appropriate management approach.
Clinical Features:
The clinical features of pleomorphic adenoma include a slow-growing, painless lump in the affected salivary gland area. The tumor can be palpated during physical examination and may cause certain symptoms, such as facial weakness, difficulty swallowing or speaking, and pain.
Radiological Features:
Radiological imaging, such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI, is essential in evaluating the size and location of the tumor. Pleomorphic adenoma typically appears as a well-circumscribed mass with mixed echogenicity on ultrasound, while on CT scan or MRI, it appears as a heterogeneous mass with areas of both solid and cystic components.
Pathological Features:
The pathological features of pleomorphic adenoma include the presence of mixed cell types, including ductal and myoepithelial cells. The tumor is encapsulated and appears as a well-circumscribed mass on histological examination. In rare cases, pleomorphic adenoma can undergo malignant transformation, which requires further treatment.
Management:
The management of pleomorphic adenoma depends on various factors, including the size and location of the tumor, the patient’s age, and their overall health. Small, asymptomatic tumors may not require treatment and may be monitored through regular imaging. Surgical removal of the tumor is the primary treatment option for larger or symptomatic tumors. In some cases, radiation therapy or chemotherapy may be necessary, especially for malignant tumors.
In summary, pleomorphic adenoma is a common type of benign tumor affecting the salivary glands. It can cause significant discomfort and disfigurement if left untreated. A proper diagnosis and management approach are essential to ensure the best possible outcome. This blog has provided a comprehensive overview of pleomorphic adenoma, including its causes, diagnostic methods, clinical and radiological features, pathological characteristics, and management options. If you suspect you have pleomorphic adenoma, seek medical attention promptly to receive the appropriate diagnosis and treatment.



Responses