Obesity
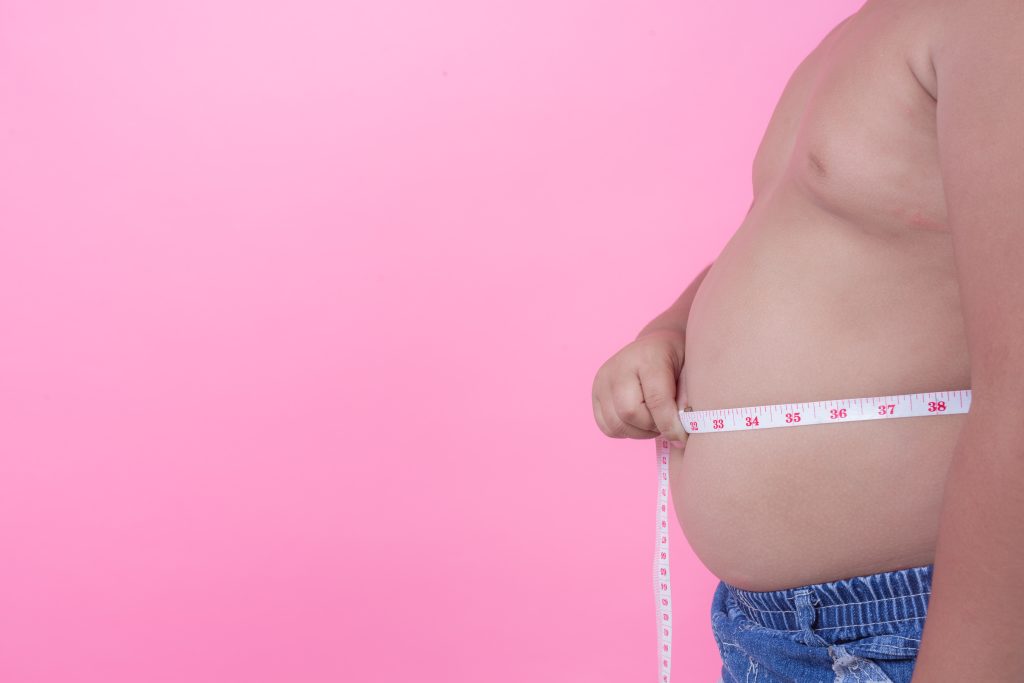

OBESITY
- WHO has defined it as excessive fat accumulation that may impair health .
- We use BMI (body mass index) to classify obesity in children > 5 years to adults.
- BMI = weight in kg/height in (meter) 2
- So obesity is BMI >30kg/m2
- Cause of obesity is accumulation of fat as a result of high caloric intake comparing to what the body can use for energy consumption.
- There are individuals more susceptible to obesity due to genetic influence on metabolism or appetite drive.
- Obesity is not only a cosmetic issue but also a health problem. It has complications starting from head to toes.
Obesity complications:
Head: Psychologically, it causes low self-esteem, depression, eating disorders (obese people have high metabolic rate, so increase appetite), low social interaction.
Neurologically; idiopathic intracranial hypertension.
Cardiovascular: hypertension, dyslipidemia, coagulopathy.
Respiratory: obstructive sleep apnea, asthma.
Gastrointestinal: gall stones ( due to increasing cholesterol ), colon cancer, non-alcoholic liver disease, gastro-oesophagal reflux disease.
Endocrine: insulin resistance which leads to type 2 diabetes, precocious puberty, polycystic ovaries in females, hormone-related cancers (like breast, prostate etc.), menstrual irregularities and infertility.
Musculoskeletal: ankle sprain, flat feet, osteoarthritis (most common) and back pain.
NOTE: some complication distribution of excess fat is important. Central obesity is highly associated with diabetes type 2 and cardiovascular diseases.
Advice:
- In obese people, more active intervention is usually required to lose weight before conversion to the ‘weight maintenance’.
- Most involve recommending a reduction of daily total energy intake of 600 kcal from the patient’s normal consumption.
- A loss of 100 kJ per day will lead to an eventual body weight change of about 1 kg, with half of the weight loss depending on person adherence to diet plan. (Davidson’s principle and practice of medicine)
Management of obesity includes dietary changes, exercise, drugs and surgery.
Note: Since obesity is a cumulative effect of energy excess, obese children usually become obese adults.
WHO has set 6 critical areas of action for ending childhood obesity.
- Promote intake of healthy foods
- Promote physical activity
- Preconception and pregnancy care
- Early childhood diet and physical activity
- Health, nutrition, and physical activity for school-age
- Children’s weight management.
“PREVENTION OF OBESITY STARTS PRECONCEPTION”
Maternal health is a significant factor for increased risk of obesity to a child, starting from preconception, during and after delivery; the health of the mother should be checked and maintained so fetal development can be good up to childhood.
Preconception counselling: as a couple (a mother and father)
Maternal health optimization includes overweight and underweight treatment, dietary counselling since the risk of obesity can be passed from one generation to another.
For diabetic mothers, sugar control should start before conception since there is an increased risk of delivery of big babies with poor sugar control. If they are using oral hypoglycemia, they should be replaced with insulin.
A woman should quit smoking, alcohol and drug abuse 3months before conceiving.
A woman needs support and care from her partner.
Most pregnancies are unplanned, so few mothers benefit from preconception counselling.
Antenatal care:
Counselling on a diet during pregnancy is essential for fetal development; caloric requirements increase during pregnancy. Obese women are advised to gain less weight since it is associated with fetal macrosomia.
A pregnancy diet should be light, easily digestible and nutritious. Supplementation is essential from the second trimester since dietetic components cannot be enough; this includes iron supplements and vitamins. Most protein and fat should be from animal products since they also contain vitamins a and d.
Postpartum care:
As in breastfeeding section explained, breast milk is vital in the early development of the child.
Counselling on exclusive breastfeeding is essential for the first six months , and after that, weaning should be continued with nutritious foods.
Provide a child with a balanced diet, physical activity, don’t give a child junky foods and snacks between meals; avoid watching TV and games all day with no physical activity.
“Obesity prevention starts with you as a couple.”



Responses