Health Benefits of Cinamon
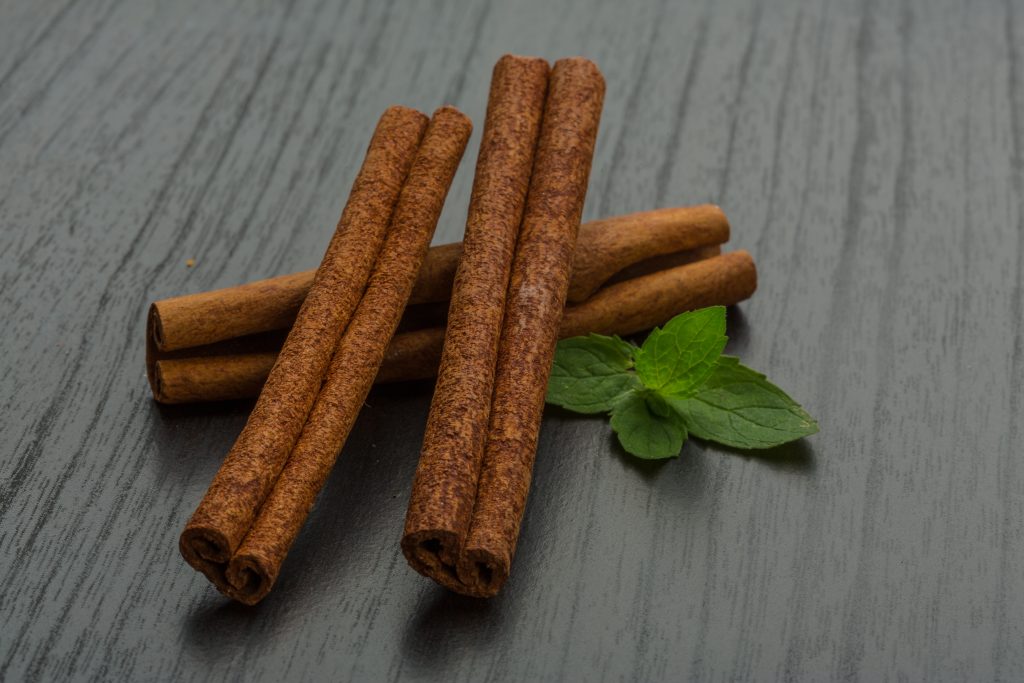

CINNAMON
An ancient aromatic spice that has a warm and pleasant taste and undoubted health benefit for centuries,
Scientific Name: Cinnamomum Verum
Synonyms: Cinnamomum Zeylanicum
Family: Lauraceae
True Cinnamon derived from the Hebraic and Arabic term ordinary, meaning fragrant spice plants,
Egyptians used cinnamon in their embalming process(preserve corpse from decay).
There is four prominent Cinnamon.
1 Cinnamomum Verum (Ceylon Cinnamon)
CeylonnCinnamon is a true Cinnamon or known as soft Cinnamon, because of its texture and is preferably used for herbal purposes; and This kind is natively cultivated in Brazil, Southern India, Sri Lanka, Mexico, Madagascar, and East Africa. They have a mildly sweet taste, Light to medium reddish brown interns of color.
Ceylon Cinnamon is one of the expensive Cinnamon in the market compared to other types; because of its high health benefits and low level of coumarin content ( coumarin is a fragrant chemical compound found in all Cinnamon and can cause liver toxicity and damage), the amount of coumarin in Ceylon Cinnamon is ) 0.017 g/kg, so established Tolerable Daily Intake (TDI) is 0.1 mg/kg body weight.
2 Cinnamomum burmannii(Korintje Cinnamon/Padang Cassia/Indonesia Cinnamon)
Indonesia is the leading producer and supplier to America, and it is very cheap compared to Ceylon Cinnamon that is one of the reasons why its so popular and used in bakeries; it has a spicy taste and powerful smell(fragrant), and it is friendly works for everything
It contains a 2.15 g/kg amount of coumarin, which is very high compare to Ceylon Cinnamon
3 Cinnamomum cassia (Saigon Cinnamon/Vietnamese Cinnamon)
This Cinnamon originated from Vietnam, which made a good impression for having a spicy and robust aroma and taste, which made it more expensive than Padang Cassia Cinnamon; the bad side is it has the highest levels of 6.97 g/kg coumarin content.
4. Cinnamomum Loureiroi (Royal cinnamon
This is one of the very spicy and super sweet Cinnamon and more challenging to find
Function of Cinnamon
The following are evidenced-based benefits(uses) of Cinnamon.
1 Antioxidant are either artificial or natural molecules that may prevent or delay cell damage from free radicals, which are highly reactive and unstable molecules produced by the body as a by-product of metabolic reactions in the body or by exposure to toxic substances, they can Damage DNA, Lipid, or cell membranes . The health effects of free radicals are associated with multiple illnesses like cancer and heart diseases, Cinnamon is a natural source of antioxidants.
2 Antiinflammatory -Cinnamon reduce inflammation or swelling,
3 Antiprostaglandins
4 Antihistamine
5 Anticonvulsant
6 Antileukemic
7 Antifungal
8 Antiseptic
9 Antipyretic
10 Bactericide ( Gram + and Gram -)
11 Anti-cancer
12 The bark in the trunk of the cinnamon tree has been used for abdominal cancers; if you chew, the bark is good for dysmenorrhea, bark infusion is good for diarrhea, nausea, for the heart, to treat enteritis and fever, biliousness, bronchitis, diarrhea, itch, parched mouth, worms, and cardiac, rectal, and urinary diseases,
13 The spicy triad (cardamom, Cinnamon, cassia) has been used for lingual paralysis, stomach cramps, and toothache.
14 The Leaves used for uterine cancer, the seeds for venereal warts, You can also grind Cinnamon with carrot, good for anemia.
15 For snoring suggest 1 cup of cinnamon tea with two teaspoons grated ginger and honey and milk added. Drink at bedtime each night until cured
Conclusion
” Nature has millions of blessings for us to stay healthy.”





Responses